Ways of transmission
3 main routes of HIV transmission:
Unprotected sexual intercourse (without condoms) with a person who is infected HIV-infection;
Exposure to infected blood – though blood transfusions, injections or other invasive procedures. Most occurs as a result of the use of the of contaminated syringes/needles during injecting drug use;
Transmission from an HIV-positive mother to her child during pregnancy, during delivery or as a result of breastfeeding.
Overwhelming evidence indicates that you cannot become infected by:
Shaking hands, hugging or kissing;
Coughing or sneezing;
Sharing food, eating or drinking utensils;
Using toilets or showers;
Using public swimming pools;
Getting a mosquito or insect bite;
Working, socializing, or living side by side with HIV-positive people.

Preventing Sexual Transmission – ABC formula.
Abstinence from sexual contacts – the best way to avoid HIV;
Be faithful to your sexual partner;
Condom use – male & female condoms are both effective in preventing HIV & other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as Hepatitis B & C, gonorrhoea, syphilis, etc. Untreated STIs significantly increase the risk of HIV transmission. Early diagnosis & treatment of STIs is essential.
Prevention during injections.
Use only new or sterilized needles and syringes during any type of injection;
No drugs, No injecting drugs, If used use single syringes & needles only – NO SHARING OF SYRINGES OR NEEDLES;
Prevention of mother to child transmission.
Georgia as most countries globally ensures that all pregnant women have access to voluntary counseling & testing on HIV with relevant treatment and care if required;
If tested positive risk of HIV transmission from mother to child can be reduced to as low as 2% by:
Antiretroviral treatment;
Selective Caesarean Section;
Appropriate counselling on Breastfeeding.
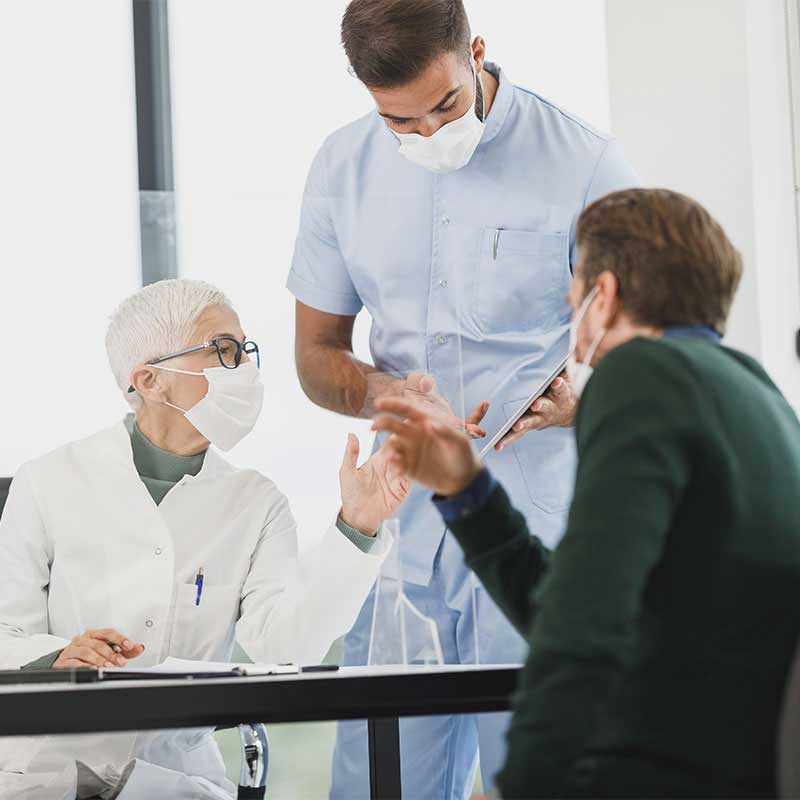
Features
High-level professional and experienced physicians work in our center
Experience
Quality
Positive
24 Hours
